|

Week
14: Air
Weeks
13, 14, and 15 make up a three-week cycle about air. Currently, you are
in Week B: Teacher As Scholar.
This week you should
refer to the resources listed under Readings & References, and you
need to complete the assignments listed under Assignments & Rubrics.
This week’s assignments focus on…
|
Individual:
-
Posting
questions about air, then finding articles and web resources
to build knowledge and background.
-
Helping
teammates to answer their questions.
Team:
|
Readings
& References
 Read:
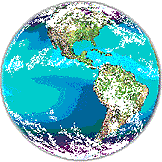
The atmosphere, "air sphere," is the envelope of air that surrounds
the whole earth. When you look at the earth from space, you usually see
lots of clouds. Rain and snow are often falling underneath the clouds,
but you need a radar to see them. Read:
The atmosphere, "air sphere," is the envelope of air that surrounds
the whole earth. When you look at the earth from space, you usually see
lots of clouds. Rain and snow are often falling underneath the clouds,
but you need a radar to see them.
Some places on Earth
(like the poles and the equator) are almost always covered by clouds.
If you look at the globe, you can see the line of clouds across the middle
that closely follows the equator. There are also clouds over the
jungles of Brazil. Lines of clouds along the leading edges of storms can
be seen in the north and south Pacific and over North America. Other places,
like the deserts in the American Southwest, are almost cloud-free.
Review:
Earth at Hand, pp. 90 and 103, and "Gone with the Wind,"
pp. 104.
Read: On your
own, read about the following
topics related
to the study of the air.
- Climate/weather
- Do plants eat air?
- Water cycle
- Global warming
(ecosystem - stability)
- Clouds and energy
(Do clouds make it warmer or cooler?)
- Seasons and energy
distribution
Read: Some
related National
Science Education Standards and Project
2061 Benchmarks for Elementary Science Education
- Air is a substance
that surrounds you, takes up space, and whose movement is felt as wind.
- Some events in
nature have a repeating pattern. The weather changes some from day to
day, but things such as temperature and rain (or snow) tend to be high,
low, or medium in the same months every year.
- Clouds and fog
are made of tiny droplets of water.
- Water cycle
in the atmosphere
- Evaporation
- condensation
- Water can be
solid or gaseous (water vapor)
- Changes in
substances
- Weather changes
from day to day and over the seasons.
- Weather can be
described by measurable quantities such as temperature, wind direction
and speed, and precipitation.
- Wind shapes and
reshapes the earth's land surface by eroding rock and soil in some areas
and depositing them in other areas, sometimes in seasonal layers.
- Changes in
the earth (slow and fast)
Recommended Web
Sites:
Assignments
& Rubrics
You will work individually and in teams to address air
during this three-week cycle. Use the links below to access the assignments
and rubrics.
Week
B: Teacher As Scholar - Individual
Earth Sphere Scholar Assignment &
Rubric
You will post your questions about air and Earth system science,
find articles and web resources to build your knowledge and background,
post your resources with annotations to Resource Space, and use what you
have learned to answer your own questions and those of your teammates.
Week
B: Teacher As Scholar - Team
Essential Question Scholar Assignment
& Rubric
You and your teammates will address the essential questions about
air.
[
Home ] [ Intro
] [ Guide ] [
Classroom ]
|